Private health insurance opens the door to a realm of healthcare coverage beyond the scope of public options. As we delve into this intricate landscape, we uncover the nuances of various plans, providers, and essential considerations that shape one's healthcare decisions.
Overview of Private Health Insurance

Private health insurance is a type of coverage that individuals can purchase to help cover medical expenses that are not covered by public health insurance plans. Unlike public health insurance, which is funded by the government and provides basic healthcare services to all citizens, private health insurance is typically purchased from private companies and offers a wider range of benefits and coverage options.
Key Features and Benefits of Private Health Insurance
Private health insurance offers several key features and benefits, including:
- Access to a wider network of healthcare providers
- Shorter wait times for specialist appointments and procedures
- Coverage for additional services not covered by public health insurance, such as dental, vision, and mental health services
- Ability to choose your own doctor and hospital
- Option to customize your coverage based on your individual needs and preferences
Examples of Private Health Insurance Providers
In the United States, some examples of private health insurance providers include:
- UnitedHealthcare
- Anthem Blue Cross Blue Shield
- Cigna
In the United Kingdom, private health insurance providers include:
- Bupa
- Axa PPP Healthcare
- VitalityHealth
Types of Private Health Insurance Plans
Private health insurance plans come in various types, each with its own coverage, costs, and limitations. Understanding the differences between these plans can help individuals choose the one that best suits their needs.
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)
- HMOs typically require members to select a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates all healthcare services.
- Coverage is limited to a network of healthcare providers, and referrals are needed to see specialists.
- HMOs generally have lower out-of-pocket costs but offer less flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
- PPOs offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, allowing members to see specialists without referrals.
- Members can also receive partial coverage for out-of-network services, but at a higher cost.
- PPOs usually have higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs compared to HMOs.
Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO)
- EPOs combine features of HMOs and PPOs, offering a network of providers like HMOs with the flexibility to see specialists without referrals like PPOs.
- However, coverage is limited to in-network providers, and out-of-network services are not covered except in emergencies.
- EPOs may have lower premiums than PPOs but higher than HMOs, with moderate out-of-pocket costs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Private Health Insurance

When choosing a private health insurance plan, there are several important factors to consider to ensure you select the right option for your needs. Understanding the impact of premiums, deductibles, coverage limits, and network providers is crucial in making an informed decision.
Here are some key factors to keep in mind:
Premiums
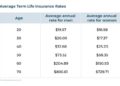
One of the first things to consider when choosing private health insurance is the monthly premium. This is the amount you will pay to maintain your coverage. While lower premiums may seem attractive, they often come with higher out-of-pocket costs when you need medical care.
On the other hand, higher premiums may provide more comprehensive coverage with lower out-of-pocket expenses. It's essential to strike a balance between affordability and coverage.
Deductibles
The deductible is the amount you must pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Plans with lower deductibles typically have higher premiums, while plans with higher deductibles have lower premiums. Consider your health needs and financial situation when choosing a plan with an appropriate deductible amount.
Coverage Limits
It's crucial to understand the coverage limits of a private health insurance plan. This includes the maximum amount the insurance will pay for specific services or treatments. Make sure the plan covers essential services you may need, such as hospital stays, prescription drugs, and preventive care.
Be aware of any exclusions or limitations that may apply.
Network Providers
Network providers are healthcare professionals, facilities, and hospitals that have agreements with the insurance company to provide services at a discounted rate. Consider whether your preferred healthcare providers are in-network to ensure you can receive care without facing higher out-of-pocket costs.
Out-of-network providers may result in higher expenses or limited coverage.
Comparing Options
When evaluating different private health insurance options, it's essential to compare the plans based on your specific needs. Look beyond just the cost and consider factors like coverage, benefits, provider networks, and customer service. Use online comparison tools, review plan documents carefully, and seek guidance from insurance professionals if needed to make an informed decision.
Coverage and Exclusions of Private Health Insurance
Private health insurance provides coverage for a wide range of medical services and treatments, offering individuals access to timely and quality healthcare. However, it's essential to understand the limitations and exclusions that come with these plans to make informed decisions about your healthcare needs.
Typical Medical Services Covered
- Doctor visits
- Hospital stays
- Prescription medications
- Laboratory tests
- Emergency care
- Mental health services
- Maternity care
Common Exclusions or Limitations
- Cosmetic procedures
- Dental care
- Long-term care
- Experimental treatments
- Pre-existing conditions
- Alternative therapies
Filing Claims and Reimbursement Policies
Understanding how to file claims and navigate reimbursement policies is crucial for maximizing the benefits of your private health insurance plan. It typically involves submitting medical bills and documentation to your insurance provider, who will then process the claim and provide reimbursement based on your coverage.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, private health insurance offers a personalized approach to healthcare, allowing individuals to tailor their coverage to suit their needs. By understanding the intricacies of different plans and providers, one can navigate this complex terrain with confidence and clarity.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the difference between private health insurance and public health insurance?
Private health insurance is purchased from private companies, while public health insurance is provided by the government.
How do premiums and deductibles impact private health insurance decisions?
Premiums are the amount you pay for insurance, while deductibles are what you must pay before your insurance kicks in.
What are common exclusions in private health insurance coverage?
Common exclusions include cosmetic procedures, experimental treatments, and pre-existing conditions.